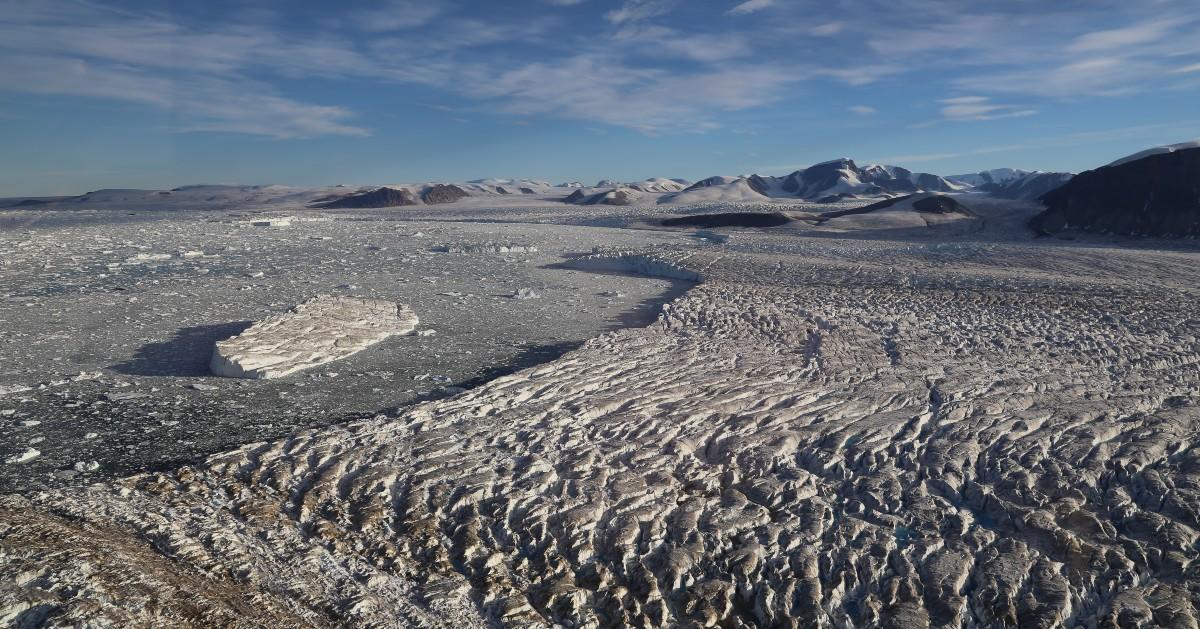
Trinity Glacier is one of the glaciers that has experienced the most retreat in the Canadian Arctic over the past 20 years, with losses of its terminus at a rate of approximately 1 km2 per year. This photograph shows a freshly calved large iceberg drifting away from the front of Trinity Glacier in August 2016.
Chilling findings
In their article "Retreat of Northern Hemisphere marine-terminating glaciers, 2000-2020" published in Geophysical Research Letters, they analyzed all 1704 glaciers that touched the ocean in the year 2000 and documented their frontal position in 2000, 2010, and in 2020.
"Since 2000, glaciers in the Northern Hemisphere that end in the ocean lost a total area of 390 km2 per year. That’s 6.6 times the area of Manhattan, or an average of more than 1 km2 per day," said lead author Will Kochtitzky, PhD candidate in the Department of Geography, Environment and Geomatics at the University of Ottawa.
According to the study, glaciers flowing from the Greenland Ice Sheet accounted for over 60% of total area losses.
“Of the 1704 glaciers that ended in the ocean in the year 2000, a total of 123 of them no longer met the ocean in 2020 due to retreat,” said Kochtitzky.
“Overall, we found that 85% of glaciers retreated, 12% did not change within uncertainty limits, and only 3% of glaciers advanced from 2000 to 2020.”
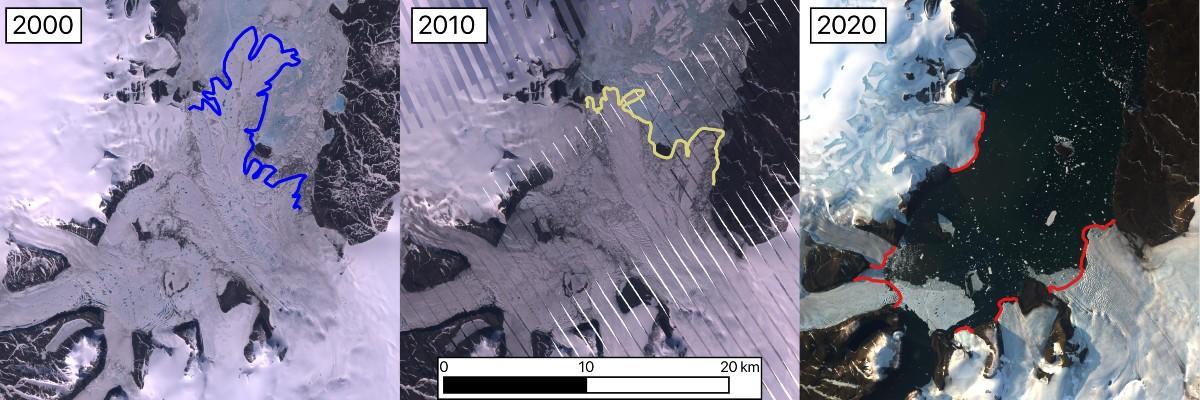
Matusevich Ice Shelf, Russia, was the ice mass with the largest loss outside of Greenland as it lost 160 km2 between 2000 and 2020. The ice shelf broke up in 2012.
Global warming
While climate change induced by human activities is broadly responsible for melting ice caps and shrinking glaciers around the world, local topographic and environmental conditions are important in explaining why some glaciers retreated more than others, according to the researchers.
“We found large variations in glacier response to similar changes in air and ocean temperature and sea ice concentrations, showing that unique glacier characteristics are the most important factor in controlling the variability of glacier retreat,” explained co-author Luke Copland, Full Professor in the Department of Geography, Environment and Geomatics at the University of Ottawa, and University Research Chair in Glaciology.
“The loss of ice shelves across the Arctic is one of the main drivers of retreat,” he added. “Glaciers which have an unusually wide margin where they meet the ocean, and those that have a bed below sea level and which gets deeper away from the coast, also saw particularly fast retreat rates.”
Of the few glaciers that defied the odds and advanced instead of retreating, most were due to “internal instabilities called surge events,” which cause the glacier to move 10 to 100 times faster than normal for a few years.
“However, glaciers that displayed large advances due to surging over the past decade are likely to experience large retreats in the next few years, with overall retreat in the long term,” said Kochtitzky.
The two researchers manually examined satellite imagery at the University of Ottawa to map the glaciers and measure the retreating.
“Prior to this study, we didn’t even know how many glaciers reached the ocean in the Northern Hemisphere, let alone understand how or why they were changing,” said Will Kochtitzky.
“This study has mapped every such glacier for the first time, and from this provided the first measure of their rates of change. This information is crucial for understanding the impacts of climate change on a hemispheric basis and will be used in future climate assessment reports such as those issued by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).”
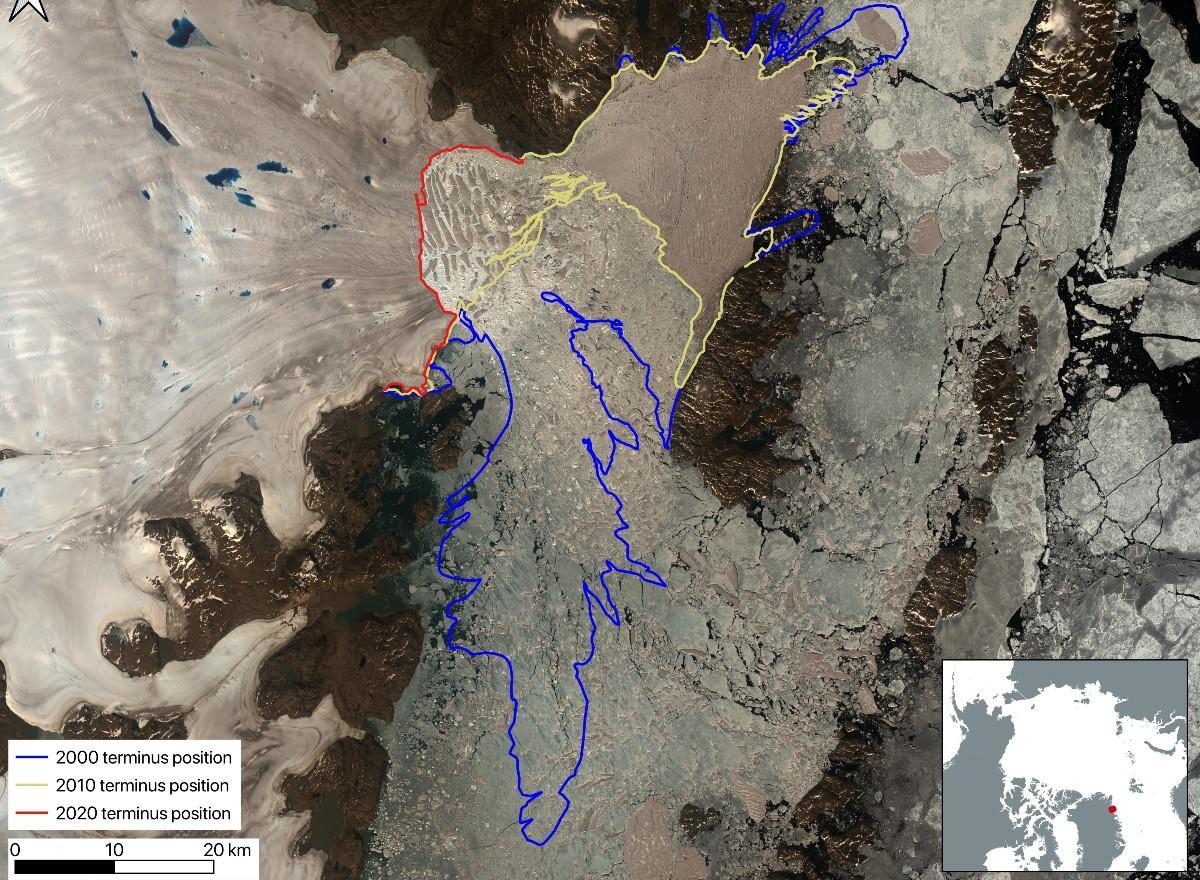
Zachariae Isstrøm, NE Greenland, has lost more area than any other glacier in the Northern Hemisphere since 2000 due to the loss of its ice shelf.
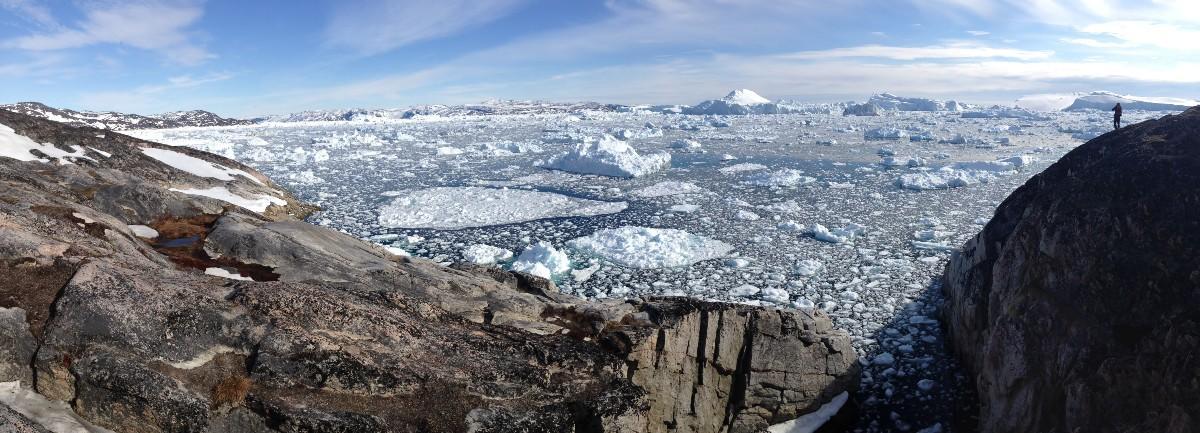

Jakobshavn Glacier, Greenland, has rapidly retreated over the past 20 years, producing large numbers of icebergs that are seen here outside of Ilulissat, Greenland, in June 2015.
Too late to turn the tide?
According to uOttawa researchers, marine-terminating glacier losses are widespread across the Northern Hemisphere, and there is little likelihood that these losses will slow down under the current climate regime.
“We have lost at least a dozen ice shelves over the past 20 years because a climate threshold has been reached beyond which these ice masses can no longer survive,” said Dr. Luke Copland.
“The few remaining ice shelves in northern Canada, Greenland, and Russia are likely to disappear in the coming decades.”
For media inquiries:
media@uottawa.ca
